Navigating Special Needs Trusts: A Guide for Seniors and Their Families
January 17, 2024
Estate Tax Planning for Montana Seniors: Strategies and Tips
January 17, 2024Elder law is a crucial field that addresses the unique legal needs of seniors and their families. As the population ages, understanding the nuances of elder law becomes increasingly important. This guide discusses the various aspects of elder law, from estate planning to long-term care and guardianship. It aims to give seniors and their families the knowledge they need to navigate these complex legal waters confidently.
Key Takeaways:
- Elder law encompasses a wide range of legal issues specifically affecting seniors.
- Key areas include estate planning, long-term care, guardianship, and understanding public benefits like Medicare and Medicaid.
- Being informed about elder law can significantly impact the quality of life and legal rights of seniors.
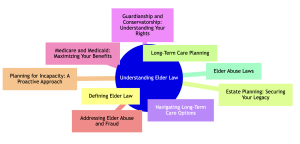
What is Elder Law?
Elder law is a specialized area of legal practice focusing on the issues that affect the aging population. This field covers a variety of topics, each addressing different aspects of the legal challenges seniors may face.
Areas of Elder Law:
| Area of Focus | Description |
| Estate Planning | Managing and bequeathing assets through wills and trusts. |
| Long-Term Care | Planning for nursing homes, assisted living, or in-home care. |
| Guardianship | Legal authority for decision-making in cases of incapacity. |
| Medicare/Medicaid | Navigating public health benefits for seniors. |
| Elder Abuse Protection | Legal remedies for abuse and fraud against seniors. |
Estate Planning: Securing Your Legacy
Estate planning is a vital component of elder law, ensuring that a senior’s assets are managed and distributed according to their wishes. It involves creating wills and trusts, establishing durable powers of attorney, and crafting advance medical directives. These tools not only ensure the proper management of assets but also protect seniors in cases of incapacity, allowing appointed individuals to make decisions on their behalf.
Estate planning is not just about distributing assets – it’s about creating a legacy and ensuring peace of mind. It’s a process that requires careful consideration and often, the guidance of a skilled elder law attorney.
Navigating Long-Term Care Options
Long-term care planning is a pivotal aspect of elder law, focusing on the needs of seniors who require ongoing assistance with daily activities. This planning is essential for ensuring that seniors receive the care they need in a setting that is both comfortable and appropriate for their situation. It involves evaluating care needs, understanding financial implications, and exploring insurance options.
Evaluating Care Needs
Assessing the level of care required is the first step in long-term care planning. This involves determining whether in-home care, assisted living, or nursing home care is most suitable based on the senior’s health status, mobility, and daily living activities. Factors like the presence of chronic illnesses, cognitive abilities, and the need for specialized care play a crucial role in this decision-making process.
Financial Planning for Long-Term Care
Understanding the costs associated with different care options is a critical component of long-term care planning. This includes the direct costs of care facilities or in-home care services and ancillary expenses like medications, medical equipment, and personal care supplies.
Seniors and their families need to plan for these expenses, considering their current assets, income streams, and potential for financial assistance from programs like Medicaid.
Insurance Considerations
- Medicare and Medicaid: Understanding how these programs can contribute to covering long-term care costs. Medicare generally covers short-term care, while Medicaid may cover longer-term care for eligible individuals.
- Long-Term Care Insurance: Evaluating the benefits and limitations of long-term care insurance policies, which can significantly offset the costs of long-term care services.
- Other Insurance Policies: Exploring other insurance options like life insurance with long-term care riders or hybrid policies that combine life insurance with long-term care benefits.
Effective long-term care planning helps seniors and their families make informed decisions about care, balancing personal preferences with practical considerations. It’s about finding the right care solution that aligns with both the senior’s needs and the family’s financial capabilities, ensuring a comfortable and dignified life in the later years.
Guardianship and Conservatorship: Understanding Your Rights
Guardianship and conservatorship are critical aspects of elder law, particularly when an individual can no longer make decisions due to physical or cognitive impairments. These legal processes involve the appointment of a guardian or conservator to make personal, financial, or medical decisions on behalf of the incapacitated individual.
Understanding the responsibilities and limitations of these roles is essential. Guardianship typically refers to the authority over personal and healthcare decisions, while conservatorship deals with financial decisions. The process for establishing these roles varies by jurisdiction but generally involves a court petition and a determination of the individual’s capacity.
Alternatives to guardianship and conservatorship, such as powers of attorney and advance directives, offer more control and should be considered in the early planning stages. These tools allow individuals to designate someone they trust to manage their affairs if they become unable to do so themselves.
Medicare and Medicaid: Maximizing Your Benefits
| Aspect | Medicare | Medicaid |
| Definition | A federal health insurance program primarily for people aged 65 and older. | A state and federal program offering health coverage to low-income individuals of all ages. |
| Eligibility and Enrollment | Available to individuals 65 and older, and to some younger individuals with disabilities. Involves understanding Parts A (hospital insurance), B (medical insurance), C (Medicare Advantage), and D (prescription drug coverage). | Eligibility is based on income and varies by state. Includes financial and medical requirements, with a focus on providing coverage for low-income individuals and families. |
| Coverage Details | Covers hospital stays, outpatient medical services, and, in some cases, prescription drugs. Does not typically cover long-term care. | Broad coverage including hospital stays, doctor visits, long-term care, and sometimes dental, vision, and hearing services. |
| Planning Considerations | Important to understand the enrollment periods and coverage options to avoid late enrollment penalties and ensure adequate health coverage. | Involves asset and income planning to meet eligibility criteria, especially for seniors seeking long-term care coverage. |
| Asset Protection | Not directly related to asset protection but important for managing healthcare costs in retirement. | Involves strategies to protect assets while remaining eligible for Medicaid, particularly for long-term care needs. This may include trusts, spend-down strategies, and other legal tools. |
Elder law attorneys can provide invaluable assistance in this area, offering guidance on eligibility, coverage options, and planning strategies to maximize benefits and protect assets. (1)
Addressing Elder Abuse and Fraud
Elder abuse and fraud prevention is a significant area of concern in elder law. It involves safeguarding seniors from various forms of abuse and providing legal remedies for those who have been victimized. Understanding the types of elder abuse, the legal protections available, and the mechanisms for reporting abuse is crucial for protecting the well-being and dignity of seniors.
Types of Elder Abuse
Elder abuse can manifest in several forms, each causing significant harm to the senior involved. These include:
- Physical and Emotional Abuse: This encompasses any act that causes physical harm or emotional distress to a senior, such as physical assault, verbal harassment, or psychological manipulation.
- Financial Abuse: This involves the illegal or unauthorized use of a senior’s funds, property, or assets. It can include theft, fraud, misuse of a senior’s assets, or coercion in financial decisions.
- Neglect: This is the failure to provide necessary care to a senior, leading to harm or distress. Neglect can be intentional or due to the caregiver’s inability to provide adequate care.
Legal Protections and Recourse
Seniors have legal protections against abuse, and there are several avenues for seeking justice and compensation:
- Protection Orders: Courts can issue orders to protect seniors from physical, emotional, or financial abuse.
- Restitution and Compensation: Legal actions can lead to restitution for financial losses and compensation for physical and emotional damages.
- Criminal Prosecution: In severe cases, perpetrators of elder abuse can face criminal charges, providing a strong deterrent against such acts.
Reporting Mechanisms
- Hotlines and Support Services: Dedicated hotlines and support services are available for reporting elder abuse.
- Legal Assistance: Elder law attorneys can guide seniors and their families through the process of reporting abuse and seeking justice.
- Collaboration with Authorities: Elder law attorneys often work in collaboration with local authorities and social services to ensure comprehensive protection for seniors.
Understanding and utilizing elder abuse laws and reporting mechanisms empowers seniors and their families to take decisive action against abuse, ensuring that seniors live in safety and dignity. It is an essential aspect of elder law, providing a framework for addressing and preventing abuse and neglect.
Planning for Incapacity: A Proactive Approach
Incapacity planning is a proactive measure in elder law, addressing the possibility of physical or mental incapacity due to aging or illness. It involves creating legal documents that outline a senior’s preferences for financial and health care decisions in the event they can no longer make these decisions themselves.
Key elements of incapacity planning include:
- Durable Power of Attorney: This allows a designated individual to manage financial affairs.
- Health Care Proxy or Power of Attorney: This designates someone to make medical decisions on the senior’s behalf.
- Living Wills: These outline wishes for medical treatments and life-sustaining measures.
Incapacity planning gives seniors control over their future, ensuring their wishes are respected and reducing the burden on family members. It’s a crucial step in safeguarding one’s dignity and autonomy in later years.
Conclusion: Empowering Seniors and Families
Elder law is a comprehensive field that plays a crucial role in protecting the rights and well-being of seniors. From estate planning and incapacity planning to navigating Medicare/Medicaid and addressing elder abuse, understanding elder law is essential for seniors and their families. By being informed and proactive, seniors can ensure their rights are protected, their wishes are respected, and they maintain their dignity and quality of life in their later years.
This guide serves as a basic resource, providing valuable insights into the various aspects of elder law. Seniors and their families are encouraged to seek the advice of an elder law attorney to navigate these complex legal waters and make informed decisions for the future. If you or someone you know is in need of an elder law attorney, Montana Elder Law provides the best legal service any Montana senior could hope for. Call today and see, you’ll be treated like family from the start.
Reference:
(1) What Is Elder Law: And Why Do You Care?, American Bar Association, https://www.americanbar.org/groups/senior_lawyers/publications/voice_of_experience/2019/august-2019/what-is-elder-law-and-why-care/