Elder Abuse: How to Identify the Signs and What to Do
December 15, 2023
Power of Attorney in Montana: Everything You Need to Know
January 2, 2024Planning for a nursing home in Montana involves more than just selecting a facility; it’s a complex process that can be tightly connected to Medicaid eligibility, legal considerations, and financial planning.
This comprehensive guide aims to simplify this process, focusing on Medicaid’s role in long-term care and how Montana residents can navigate the system effectively.
Key Takeaways
- Planning for a nursing home in Montana can be closely linked with Medicaid, the primary source of financial assistance for long-term care.
- Understanding Medicaid’s specific eligibility criteria in Montana is crucial for effective long-term care planning.
- Legal consultation is often necessary to navigate the complexities of Medicaid and to preserve assets effectively.
Planning for a Nursing Home in Montana
Long-term care in Montana has been designed to be accessible and effective.
The state has specific regulations and programs designed to assist residents in covering the high costs associated with nursing home care.
Medicaid is a crucial component of nursing home planning in Montana.
It serves as the primary source of financial assistance for those who cannot afford the steep costs of long-term care. To qualify for Medicaid-funded nursing home care, you must meet certain income and asset limitations, which differ for individuals and couples.
Steps for Effective Planning
- Assessment of Needs: Determine the level of care required – whether it’s skilled nursing, assisted living, or independent living.
- Financial Planning: Assess your financial resources to understand how much you can afford and how Medicaid can fill the gaps.
- Legal Consultation: Consult a Montana elder law attorney to help you navigate the complexities of Medicaid eligibility and asset preservation.
Available Programs
- Home and Community-Based Services (HCBS): Provides alternatives to nursing home care, such as home health services.
- Big Sky Rx Program: Assists with prescription drug costs – another significant expense for many nursing home residents.
Considerations for Couples
If you’re married, Medicaid considers the assets and income of both spouses when determining eligibility for nursing home care.
However, the “community spouse” is allowed to keep a certain amount of assets and income without affecting the eligibility of the spouse who needs nursing home care.
What is Medicaid?
Medicaid is a joint federal and state program designed to provide healthcare coverage to low-income individuals and families.
While the federal government sets the basic framework, states like Montana have the flexibility to tailor the program to their residents’ needs.
Federal vs. State Roles
- Federal Government: Sets the basic eligibility criteria and provides a significant portion of the funding.
- State Government: Fine-tunes the program to address local healthcare needs and manages the distribution of benefits.
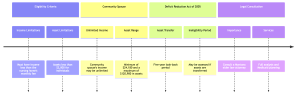
Eligibility Criteria in Montana
Table 1: Key Medicaid Criteria and Their Impact on Eligibility (1)
| Criteria | Individual | Community Spouse | Impact on Eligibility |
| Income | Must be less than the nursing home’s monthly fee | Unlimited | Major |
| Assets | Less than $2,000 | $24,180 – $120,900 | Major |
| Residence | One allowed | One allowed | Excluded from asset limitations |
| Automobile | One allowed | One allowed | Excluded from asset limitations |
To qualify for Medicaid in Montana, applicants must meet specific income and asset limitations. These criteria are designed to ensure that the program’s limited resources go to those who need them the most.
Income Limitations
- Individuals: Must have an income less than the cost of the nursing home’s monthly fee.
- Couples: Combined income must also be below the nursing home’s monthly fee.
Asset Limitations
- Individuals: Allowed to have assets less than $2,000.
- Couples: Permitted to have up to $3,000 in assets.
Exclusions from Asset Limitations
- One residence
- One automobile
- Personal property
- Household furnishings
- Prepaid irrevocable funeral and burial arrangements
The Role of the “Community” Spouse
In Medicaid parlance, a “community” spouse refers to the spouse of a nursing home resident who is not living in a nursing home. The income and assets of the community spouse can significantly impact Medicaid eligibility.
Unlimited Income
The community spouse is allowed to have an unlimited income, which does not affect the nursing home resident’s Medicaid eligibility.
Asset Range
The community spouse is permitted to have a minimum of $24,180 and a maximum of $120,900 in assets.
The Deficit Reduction Act of 2005
The Deficit Reduction Act of 2005 (DRA) introduced significant changes to Medicaid eligibility, particularly concerning asset transfers.
Understanding these changes is crucial for effective Medicaid planning.
Asset Transfer Rules
- Five-Year Look-Back Period: Any asset transfers made within five years before applying for Medicaid can result in an ineligibility period.
- Ineligibility Period: During this time, Medicaid benefits will be denied.
Cautionary Steps
- Full Analysis: Consult a Montana elder law attorney before making any asset transfers.
- Legal Techniques: Various legal techniques can protect and preserve assets while still maintaining Medicaid eligibility.
Planning Ahead: Why You Need a Montana Elder Law Attorney for Nursing Home Pre-Planning
When it comes to nursing home pre-planning in Montana, the complexities extend beyond just selecting a facility and understanding Medicaid.
This is where the expertise of a Montana elder law attorney becomes indispensable.
Importance of Legal Consultation in Nursing Home Pre-Planning
- Asset Preservation: An elder law attorney can guide you through legal avenues to protect your assets, ensuring that you can pass on your legacy while still qualifying for Medicaid benefits.
- Application Process: The Medicaid application process is notoriously complex. An attorney can help you navigate this, increasing your chances of approval and thereby securing quality long-term care.
Services Offered for Nursing Home Pre-Planning
- Asset Analysis: A comprehensive review of your financial situation is the first step in effective nursing home pre-planning. An elder law attorney can provide this – along with strategies to preserve your assets.
- Medicaid Planning: Tailored strategies to maximize Medicaid benefits – including how to allocate assets and income in a way that meets Medicaid’s strict eligibility criteria – can set you on the path to a secure future.
By engaging the services of a Montana elder law attorney, you’re not just planning for a nursing home – you’re planning for a secure, well-managed future that takes into account the complexities of Medicaid and asset preservation.
Conclusion
Planning for a nursing home in Montana is a multifaceted endeavor that requires a deep understanding of both state-specific regulations and Medicaid eligibility criteria. From assessing the level of care needed to financial planning and legal consultation, each step is crucial for a smooth transition into long-term care. Medicaid serves as a vital financial cornerstone in this planning, making it essential for Montana residents to understand its intricacies. By taking a proactive approach and seeking professional advice, you can secure quality care for yourself or your loved ones while preserving your hard-earned assets. If you or a loved one is in need of expert advice for nursing home planning in Montana, give the trusted attorneys at Montana Elder Law a call. Montana Elder Law is a dedicated resource for anyone seeking retirement planning in this wonderful state.
Reference
Montana Department of Public Health and Human Services, https://dphhs.mt.gov/